- Published on
Reciprocal Reading: Your Ultimate Guide to Strategies, Benefits, and Classroom Implementation
Reciprocal Reading: Your Ultimate Guide to Strategies, Benefits, and Classroom Implementation
Searches for "reciprocal reading" primarily indicate an informational intent, with users—such as educators, literacy specialists, teachers, or teacher trainees—seeking definitions, strategies, examples, and practical applications of reciprocal reading as a comprehension method. Based on web data, this keyword reflects a demand for resources on collaborative reading techniques that involve students taking turns in roles like predicting, questioning, clarifying, and summarizing to enhance understanding of texts, often in K-12 or literacy intervention settings for improving student engagement and skills.
Whether you're a teacher looking to boost reading comprehension or an educator exploring cooperative strategies, this guide covers reciprocal reading's principles, steps, and benefits to help you create effective literacy lessons.
What Is Reciprocal Reading?
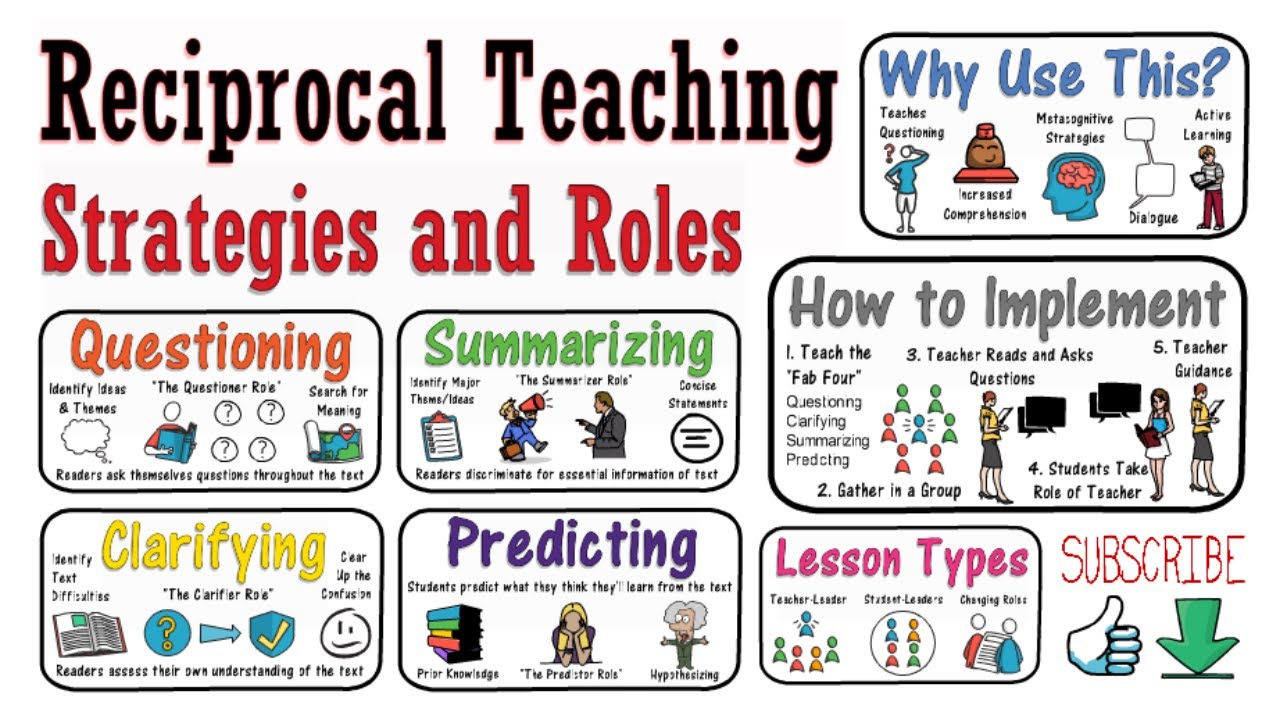
Reciprocal reading is a collaborative instructional strategy designed to improve reading comprehension by having students take turns leading discussions on a text. Similar to reciprocal teaching, it involves four key roles: predictor (anticipating content), questioner (generating questions), clarifier (resolving confusion), and summarizer (condensing main ideas). Developed as an extension of reciprocal teaching by Palincsar and Brown, reciprocal reading empowers students to actively process text, fostering metacognitive skills and peer learning. It's particularly effective for struggling readers and can be used in small groups or whole classes across subjects.
This method transforms passive reading into an interactive process, promoting deeper understanding and retention.

Visual Framework for Reciprocal Reading Strategy
Key Components of Reciprocal Reading
Reciprocal reading revolves around four core components that students learn and apply in groups:
Predicting: Students forecast what might happen next based on prior knowledge or clues in the text, activating schema.
Questioning: Generate questions to explore meaning, encouraging inquiry and focus on key details.
Clarifying: Identify and resolve confusing elements, such as vocabulary or concepts, to ensure understanding.
Summarizing: Condense the text's main points, reinforcing comprehension and retention.
These components are taught explicitly, then practiced collaboratively, making reading a social, active experience.
Step-by-Step Guide to Reciprocal Reading
How to Implement Reciprocal Reading in Your Classroom
Implementing reciprocal reading involves a gradual release of responsibility:
- Introduce the Strategy: Explain the four roles with examples and modeling.
- Guided Practice: Lead group discussions, assigning roles and providing support.
- Group Work: Divide students into small groups to rotate roles while reading.
- Monitor and Support: Circulate to offer feedback and scaffold as needed.
- Independent Application: Encourage students to use the strategy on their own or in pairs.
This approach is adaptable for various grade levels and texts, with research showing improved comprehension and engagement.

Implementing Reciprocal Reading in Your Classroom
Benefits of Reciprocal Reading
Reciprocal reading enhances comprehension, metacognition, and collaboration by making students active participants. It improves academic achievement, particularly for struggling readers, fosters critical thinking, and promotes a positive classroom dynamic. Studies confirm its effectiveness in building literacy skills and confidence.
Research-Based Benefits of Reciprocal Reading Strategy
FAQ: Common Questions About Reciprocal Reading
This Q&A addresses frequent queries based on search trends for "reciprocal reading."
What is reciprocal reading?
Reciprocal reading is a collaborative strategy where students take turns leading text discussions using predicting, questioning, clarifying, and summarizing to boost comprehension.
What are the four components of reciprocal reading?
The four components are predicting (forecasting content), questioning (generating inquiries), clarifying (resolving confusion), and summarizing (condensing key points).
How does reciprocal reading improve comprehension?
It encourages active engagement, metacognitive awareness, and peer teaching, leading to deeper understanding and retention of text.
Is reciprocal reading suitable for all ages?
Yes, it's adaptable for elementary to high school, with modifications for younger learners focusing on simpler roles.
Where can I find resources for reciprocal reading?
Resources include infographics on Pinterest and tutorials on YouTube for strategies and examples.
Comprehensive Resources for Reciprocal Reading
Students Engaging in Reciprocal Reading Activities
Conclusion: Empower Literacy with Reciprocal Reading
Reciprocal reading transforms reading instruction by making it interactive and student-led. By incorporating its components, educators can foster stronger comprehension skills. Explore the resources above to implement it today.
Complete Practical Demonstration of Reciprocal Reading Strategy